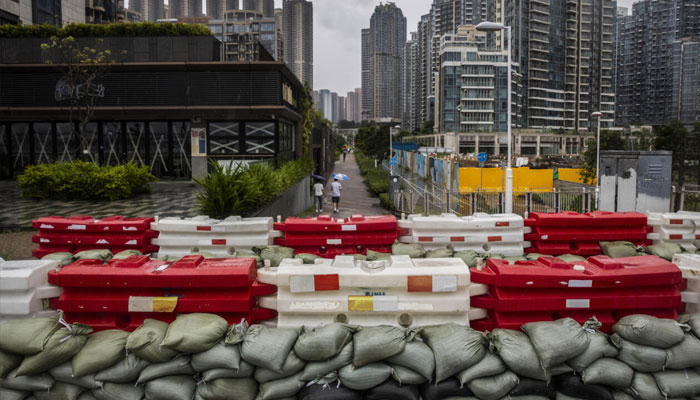
Coastal cities alarmingly slow to adapt to climate change
PARIS: Coastal cities are not doing enough to adapt to climate change, taking too long and implementing insufficient measures, according to a major study published this week.
While flood barriers and pumping systems are a step in the right direction, “across all regions and income groups, scientifically reported adaptation in coastal cities remains at rather low depth, scope and speed,” said the study published in Nature Cities, which looked at 199 cities worldwide.
Given the high exposure and vulnerability of many coastal cities, “this finding is alarming as adaptation to future climate change will require many cities to go beyond business as usual risk management,” it said.
Short- and mid-term solutions, as many cities are implementing, could even have an adverse effect, the study warned, leading to a “lock-in and maladaptive path dependency in the long-term.”
Instead, adaptation must aim at “transformation” of cities -- a change both of infrastructure and at the institutional level.
Positive models cited in the report include Singapore, Hong Kong and several Swedish cities.
But in the majority, the study found that coastal cities focus primarily on combating sea level rise, various types of flooding, and to a lesser extent the risks posed by erosion and storms.
And for scientists such a scope is too narrow -- cities need to address other problems linked to climate change, such as heatwaves.
By comparing data from 199 cities, listed in 683 scientific articles, the researchers found that the actors driving adaptation changed according to the country and income category.
The richest coastal areas take a technological approach to dealing with climate change and the major players are institutions.
Meanwhile, lower-income cities located mainly in Africa, Asia, and South and Central America, have no other choice but to rely on a “behavioural and cultural” effort for populations to adapt.
In lower-income coastal cities, there is a lack of institutional and/or technological support, making it “more likely individuals/households are reported as prime adaptation actors.”
The poorest economies remain under-represented in the scientific literature, which complicates their adaptation. “A considerable gap in research that needs to be addressed urgently,” the study warned.
-
 Real Reason Kim Kardashian Is Dating Lewis Hamilton
Real Reason Kim Kardashian Is Dating Lewis Hamilton -
 Rihanna Leaves Elderly Woman Star-struck In Viral Grocery Store Video
Rihanna Leaves Elderly Woman Star-struck In Viral Grocery Store Video -
 TikTok US Launches Local Feed Using Precise Location Data
TikTok US Launches Local Feed Using Precise Location Data -
 Jill Biden’s Former Husband Charged With Wife’s Murder
Jill Biden’s Former Husband Charged With Wife’s Murder -
 Zayn Malik Reveals Parenting Decision Gigi Hadid Criticized Him Over
Zayn Malik Reveals Parenting Decision Gigi Hadid Criticized Him Over -
 Palace Releases Prince William's Photos From Final Day Of His Saudi Arabia Visit
Palace Releases Prince William's Photos From Final Day Of His Saudi Arabia Visit -
 Microsoft Warns Of AI Double Agents As Enterprise Adoption Of AI Agents Surges
Microsoft Warns Of AI Double Agents As Enterprise Adoption Of AI Agents Surges -
 Kate Middleton, Prince William Break Silence Over Tragic Shooting In Canada
Kate Middleton, Prince William Break Silence Over Tragic Shooting In Canada -
 'Finding Her Edge' Star Madelyn Keys Explains Adriana's Remarks About Brayden Romance
'Finding Her Edge' Star Madelyn Keys Explains Adriana's Remarks About Brayden Romance -
 Royal Expert Raises Questions Over Sarah Ferguson's 'plotting' Stunning Comeback
Royal Expert Raises Questions Over Sarah Ferguson's 'plotting' Stunning Comeback -
 Instagram Develops AI ‘Create My Likeness’ Tool To Generate Personalised Photos And Videos
Instagram Develops AI ‘Create My Likeness’ Tool To Generate Personalised Photos And Videos -
 Meghan Markle, Prince Harry Friends Suggest Their Marriage 'isn't All It Seems'
Meghan Markle, Prince Harry Friends Suggest Their Marriage 'isn't All It Seems' -
 Andrew Handed Out 'classified' Information To Jeffrey Epstein
Andrew Handed Out 'classified' Information To Jeffrey Epstein -
 Margot Robbie Recalls Wild Party Days And Getting Kicked Out Of Clubs
Margot Robbie Recalls Wild Party Days And Getting Kicked Out Of Clubs -
 NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Discovers ‘Dracula Disk', 40 Times Bigger Than Solar System
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Discovers ‘Dracula Disk', 40 Times Bigger Than Solar System -
 Annular Solar Eclipse 2026: Where And How To Watch ‘ring Of Fire’
Annular Solar Eclipse 2026: Where And How To Watch ‘ring Of Fire’




