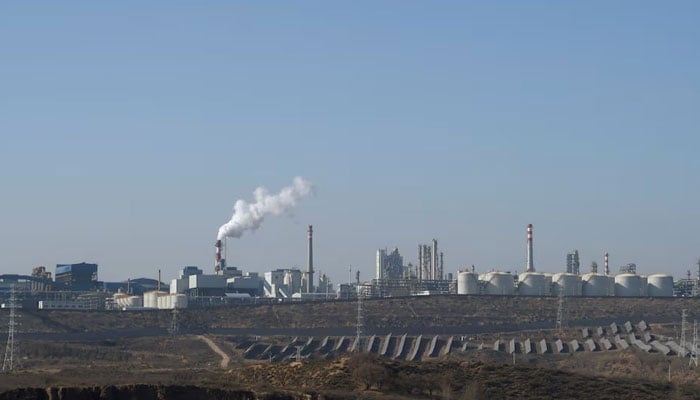
China emissions fall 3 per cent in March, may have peaked: report
BANGKOK: China’s carbon dioxide emissions fell in March for the first time since its economy reopened after pandemic restrictions, suggesting the country’s emissions may have peaked, according to a new analysis.
The March drop was the result of expanding renewable capacity, which covered almost all the growth in electricity demand, and a major slump in construction activity. If renewable capacity continues to grow at record levels, China’s emissions may have peaked in 2023, according to the analysis by Lauri Myllyvirta of the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air.
Writing for Carbon Brief, Myllyvirta said China’s carbon dioxide emissions fell three percent in March 2024 from a year earlier, based on an analysis of official data.
Emissions for the quarter were still higher, but that was because January and February 2024 were being compared to the still-sluggish period after Covid-19 restrictions were lifted in December 2022.March is “the first month to give a clear indication of the emissions trends after the rebound”, the analysis, published Tuesday, said.
While the March figure is a single data point, it tracks projections from last year and suggests key trends.Power sector emissions stabilised due to increases in solar and wind generation, while steel production dropped eight percent and cement production slumped a massive 22 percent on-year.
That reflects a slowdown in the real estate sector that is likely to continue.The growing uptake of electric vehicles, meanwhile, continues to hit demand for oil, with EVs now accounting for slightly more than 10 percent of all vehicles on the road -- up from seven percent last year, based on sales data.
Crucially, while electricity demand grew -- including at the household level because of air conditioner purchases -- almost 90 percent of the additional demand in March was covered by renewables, Myllyvirta wrote.
Much of that renewable capacity is in the form of small-scale solar, which is increasingly important in China´s renewables surge. Over the first quarter of the year, solar and wind installations were up 40 percent, though there are continued constraints on grid access for new capacity.
-
 Bangladesh Sees High Turnout In Landmark National Election
Bangladesh Sees High Turnout In Landmark National Election -
 Lufthansa Cancels Hundreds Of Flights Amid Pilot And Cabin Crew Strike
Lufthansa Cancels Hundreds Of Flights Amid Pilot And Cabin Crew Strike -
 Video: Prince Harry Tears Up Talking Of His Court Case & Children: ‘Don’t Feel Shame Even If A Judge Makes Demands'
Video: Prince Harry Tears Up Talking Of His Court Case & Children: ‘Don’t Feel Shame Even If A Judge Makes Demands' -
 King Charles Issues New Statement For ‘carers’ Two Days After Promising To Support Police Action Against Andrew
King Charles Issues New Statement For ‘carers’ Two Days After Promising To Support Police Action Against Andrew -
 Gene Simmons Makes Major Claim Against Rock & Roll Hall Of Fame
Gene Simmons Makes Major Claim Against Rock & Roll Hall Of Fame -
 Vladyslav Heraskevych Disqualified From Winter Olympics 2026 Over Helmet Controversy
Vladyslav Heraskevych Disqualified From Winter Olympics 2026 Over Helmet Controversy -
 Late James Van Der Beek Inspires Bowel Cancer Awareness Post Death
Late James Van Der Beek Inspires Bowel Cancer Awareness Post Death -
 ByteDance’s New AI Video Model ‘Seedance 2.0’ Goes Viral
ByteDance’s New AI Video Model ‘Seedance 2.0’ Goes Viral -
 Archaeologists Unearthed Possible Fragments Of Hannibal’s War Elephant In Spain
Archaeologists Unearthed Possible Fragments Of Hannibal’s War Elephant In Spain -
 Khloe Kardashian Reveals Why She Slapped Ex Tristan Thompson
Khloe Kardashian Reveals Why She Slapped Ex Tristan Thompson -
 ‘The Distance’ Song Mastermind, Late Greg Brown Receives Tributes
‘The Distance’ Song Mastermind, Late Greg Brown Receives Tributes -
 Taylor Armstrong Walks Back Remarks On Bad Bunny's Super Bowl Show
Taylor Armstrong Walks Back Remarks On Bad Bunny's Super Bowl Show -
 Pal Exposes Sarah Ferguson’s Plans For Her New Home, Settling Down And Post-Andrew Life
Pal Exposes Sarah Ferguson’s Plans For Her New Home, Settling Down And Post-Andrew Life -
 James Van Der Beek's Impact Post Death With Bowel Cancer On The Rise
James Van Der Beek's Impact Post Death With Bowel Cancer On The Rise -
 Blake Lively, Justin Baldoni At Odds With Each Other Over Settlement
Blake Lively, Justin Baldoni At Odds With Each Other Over Settlement -
 Thomas Tuchel Set For England Contract Extension Through Euro 2028
Thomas Tuchel Set For England Contract Extension Through Euro 2028