History made as Pakistan sends first mission to moon
Pakistan's first satellite mission to the moon, iCube Qamar, has been launched on board China’s Chang’E6 from Hainan, China
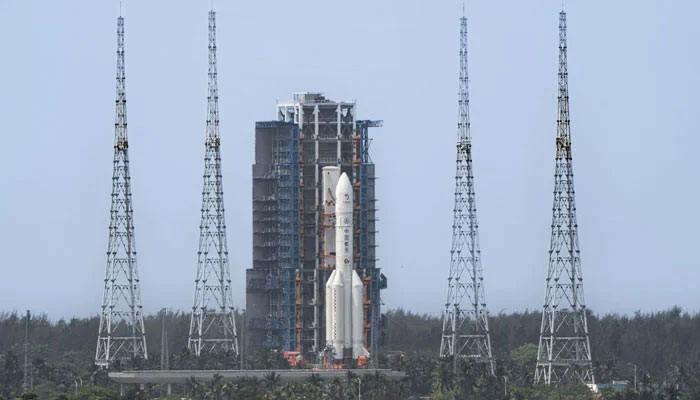
ISLAMABAD: In a historic achievement for Pakistan, the country’s first satellite mission to the moon, iCube Qamar, has been launched on board China’s Chang’E6 from Hainan, China.
The launch was telecast live on the IST website as well as the Chinese state television.
Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif felicitated the nation and scientists for launching the first lunar orbit mission.
In a statement, the PM said ICUBE-Q satellite was Pakistan’s first step in space.
The premier said Pakistani scientists, engineers and skilled workers were proving their mettle in this field like the expertise they exhibited in the nuclear technology.
He paid tribute to the core committee of the Institute of Space Technology, including Dr Khurram Khurshid, all the members of the Suparco team and students, who participated in this project.
Congratulating the students and scientists on the launch, Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister Ishaq Dar said, “Today’s launch from Hainan in China is a good example of countries and organisations coming together for space cooperation and shared benefits.”
Dr Khurram Khurshid, a member of the Core Committee at the Institute of Space Technology (IST), told Geo News that Pakistan’s satellite will reach the lunar orbit in five days and will circle around the moon for three to six months.
He said different pictures of the surface of the moon will be taken with the help of satellite after which Pakistan will have its own satellite images of the moon for research.
The satellite has been designed and developed by the IST in collaboration with China’s Shanghai University and Suparco.
Chang’6 will touch down on the moon’s far side to collect samples from the surface and return to earth for research.
-
 BTS Moments Of Taylor Swift's 'Opalite' Music Video Unvieled: See Photos
BTS Moments Of Taylor Swift's 'Opalite' Music Video Unvieled: See Photos -
 Robin Windsor's Death: Kate Beckinsale Says It Was Preventable Tragedy
Robin Windsor's Death: Kate Beckinsale Says It Was Preventable Tragedy -
 Rachel Zoe Shares Update On Her Divorce From Rodger Berman
Rachel Zoe Shares Update On Her Divorce From Rodger Berman -
 Kim Kardashian Officially Takes Major Step In Romance With New Boyfriend Lewis Hamilton
Kim Kardashian Officially Takes Major Step In Romance With New Boyfriend Lewis Hamilton -
 YouTube Tests Limiting ‘All’ Notifications For Inactive Channel Subscribers
YouTube Tests Limiting ‘All’ Notifications For Inactive Channel Subscribers -
 'Isolated And Humiliated' Andrew Sparks New Fears At Palace
'Isolated And Humiliated' Andrew Sparks New Fears At Palace -
 Google Tests Refreshed Live Updates UI Ahead Of Android 17
Google Tests Refreshed Live Updates UI Ahead Of Android 17 -
 Ohio Daycare Worker 'stole $150k In Payroll Scam', Nearly Bankrupting Nursery
Ohio Daycare Worker 'stole $150k In Payroll Scam', Nearly Bankrupting Nursery -
 Michelle Yeoh Gets Honest About 'struggle' Of Asian Representation In Hollywood
Michelle Yeoh Gets Honest About 'struggle' Of Asian Representation In Hollywood -
 Slovak Fugitive Caught At Milano-Cortina Olympics To Watch Hockey
Slovak Fugitive Caught At Milano-Cortina Olympics To Watch Hockey -
 King Charles Receives Exciting News About Reunion With Archie, Lilibet
King Charles Receives Exciting News About Reunion With Archie, Lilibet -
 Nvidia Expands AI Infrastructure With Nevada Data Centre Lease
Nvidia Expands AI Infrastructure With Nevada Data Centre Lease -
 Royal Family Shares Princess Anne's Photos From Winter Olympics 2026
Royal Family Shares Princess Anne's Photos From Winter Olympics 2026 -
 Tori Spelling Feels 'completely Exhausted' Due To THIS Reason After Divorce
Tori Spelling Feels 'completely Exhausted' Due To THIS Reason After Divorce -
 SpaceX Successfully Launches Crew-12 Long-duration Mission To ISS
SpaceX Successfully Launches Crew-12 Long-duration Mission To ISS -
 PlayStation State Of Play February Showcase: Full List Of Announcements
PlayStation State Of Play February Showcase: Full List Of Announcements




