Scientists discover strange diamond from 4.5 billion years ago
Scientists believe Lonsdaleite was replaced by diamond we see today when planet's temperature cooled and pressure lowered
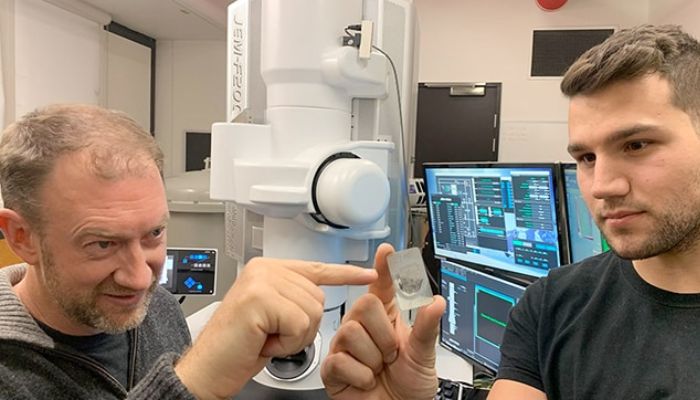
Scientists from the UK and Australia revealed that they have found a diamond from a dwarf planet on Earth.
Andy Tomkins, a geologist and professor at Monash University in Australia, found the strangely "bent" space rock when he was working on categorising meteorites, according to the co-author of the study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Alan Salek.
Further investigation revealed that the part of the diamond was actually a rare hexagonal stone called lonsdaleite.
Lonsdaleite is believed to be produced under moderate pressure and high temperature. Scientists believed that it was replaced by a diamond when the planet's temperature cooled.
In an article published by RMIT University, experts said they believe that a dwarf planet as small as an asteroid collided with the Earth over 4 billion years ago.
The collision gave birth to a unique hexagonal structure which makes it even harder than most diamonds on Earth. Our diamonds have a cubic structure.
Experts believe that the diamond is not a jewel but could actually b used to make tiny machine parts.
-
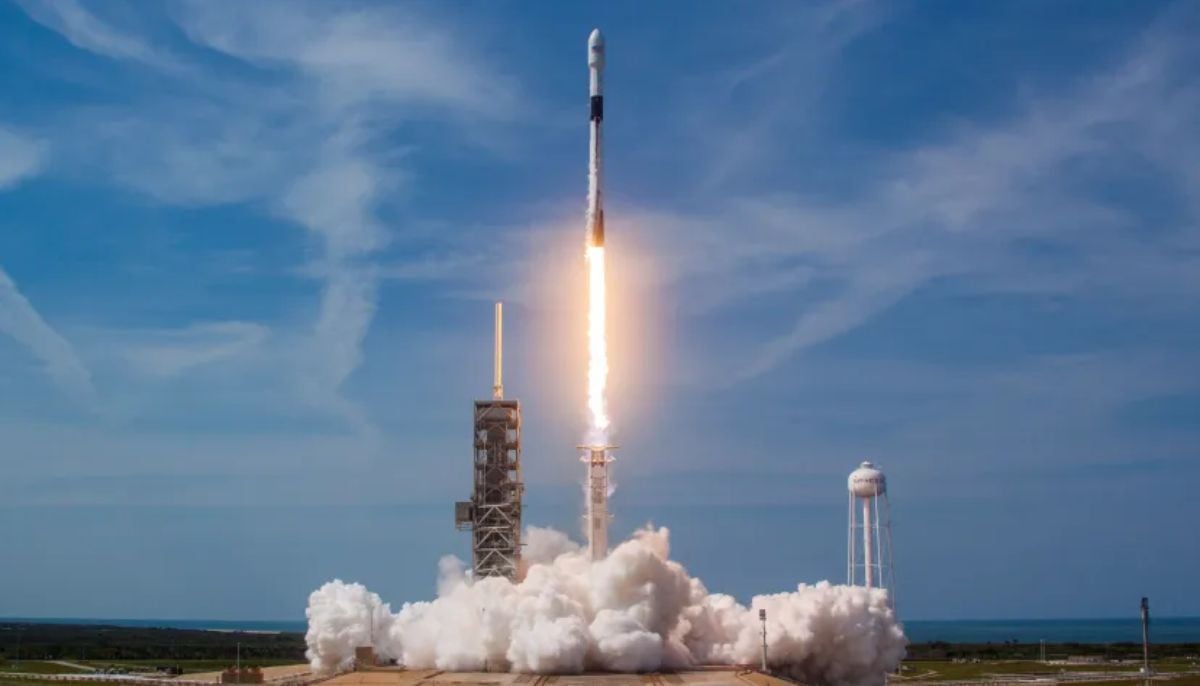
SpaceX cleared for NASA Crew-12 launch after Falcon 9 review
-
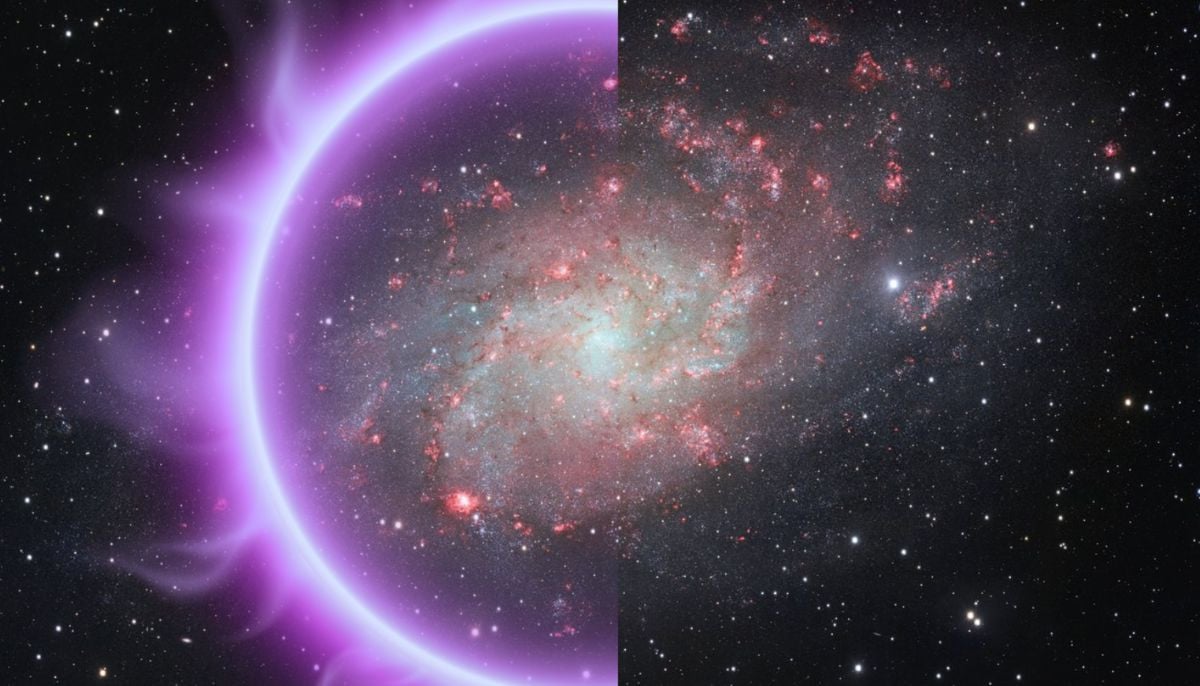
Is dark matter real? New theory proposes it could be gravity behaving strangely
-
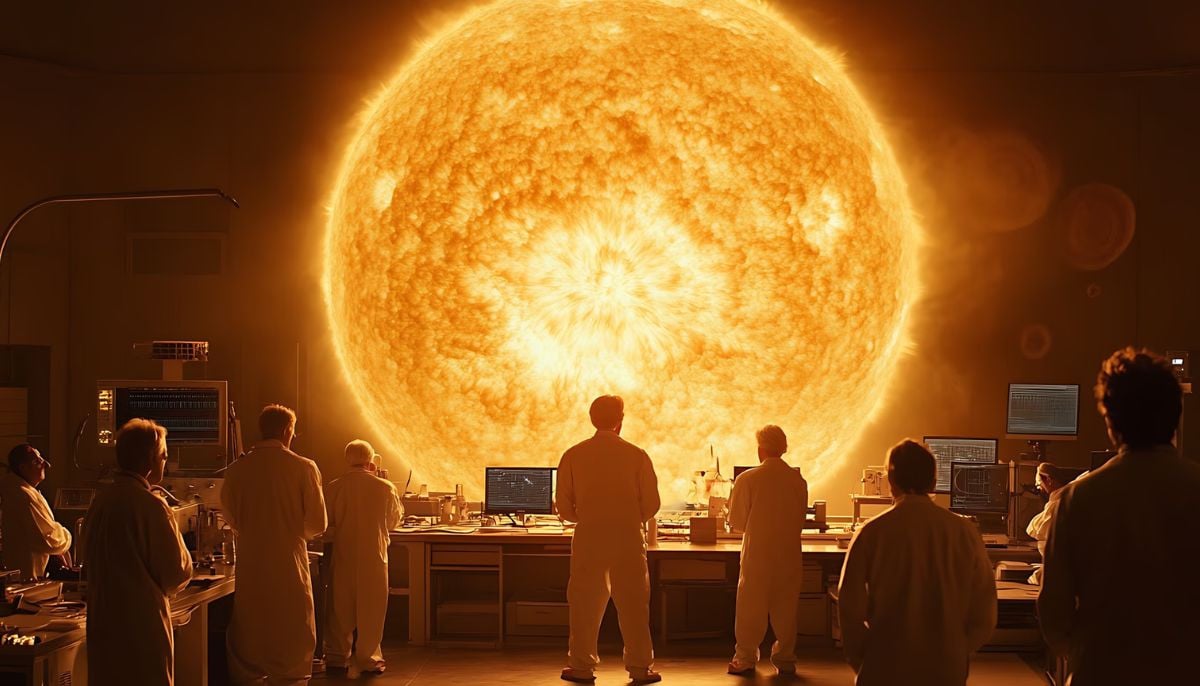
Shanghai Fusion ‘Artificial Sun’ achieves groundbreaking results with plasma control record
-
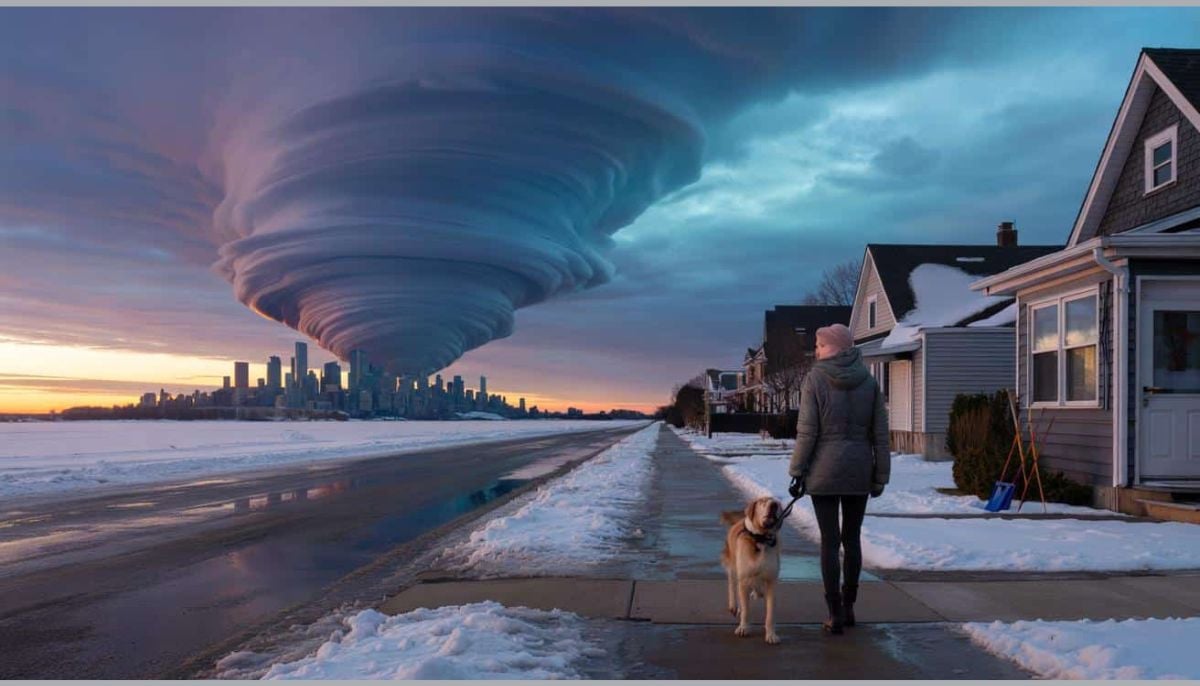
Polar vortex ‘exceptional’ disruption: Rare shift signals extreme February winter
-
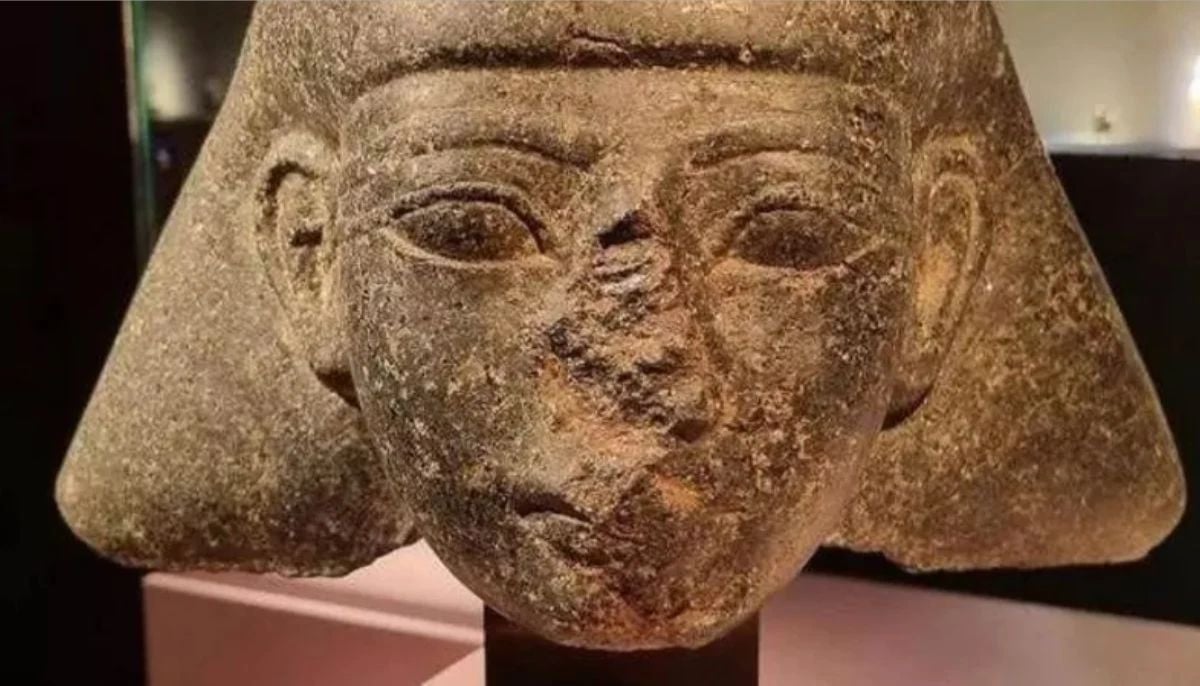
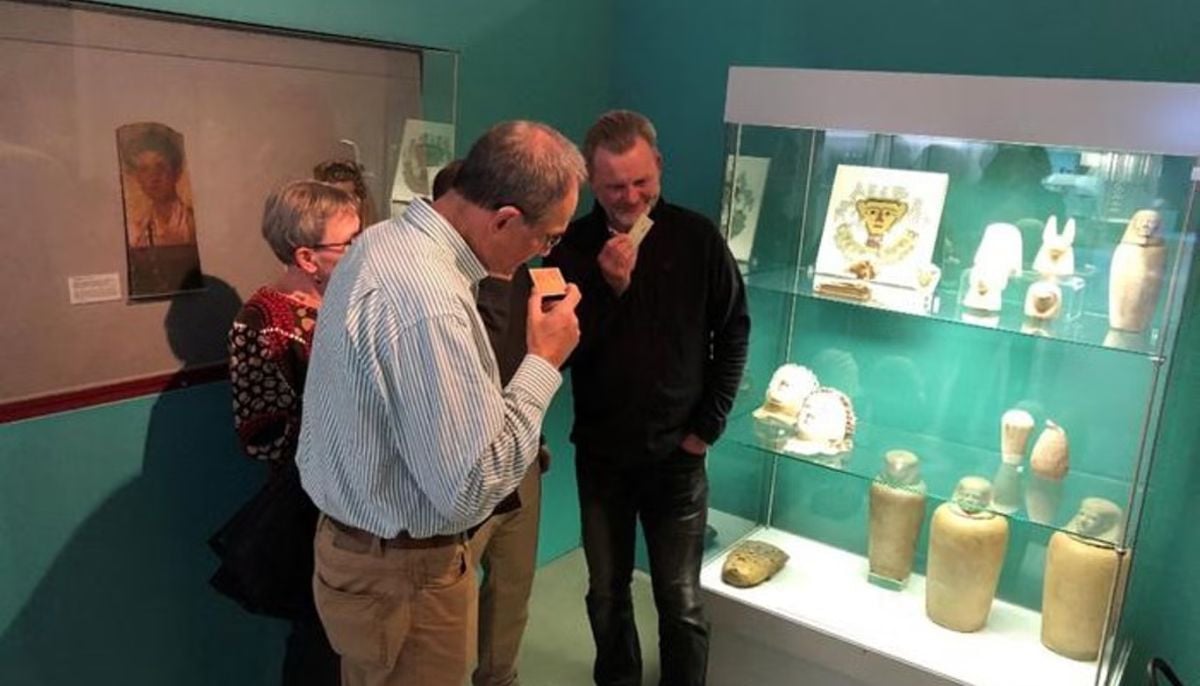
Netherlands repatriates 3500-year-old Egyptian sculpture looted during Arab Spring
-
Archaeologists recreate 3,500-year-old Egyptian perfumes for modern museums
-
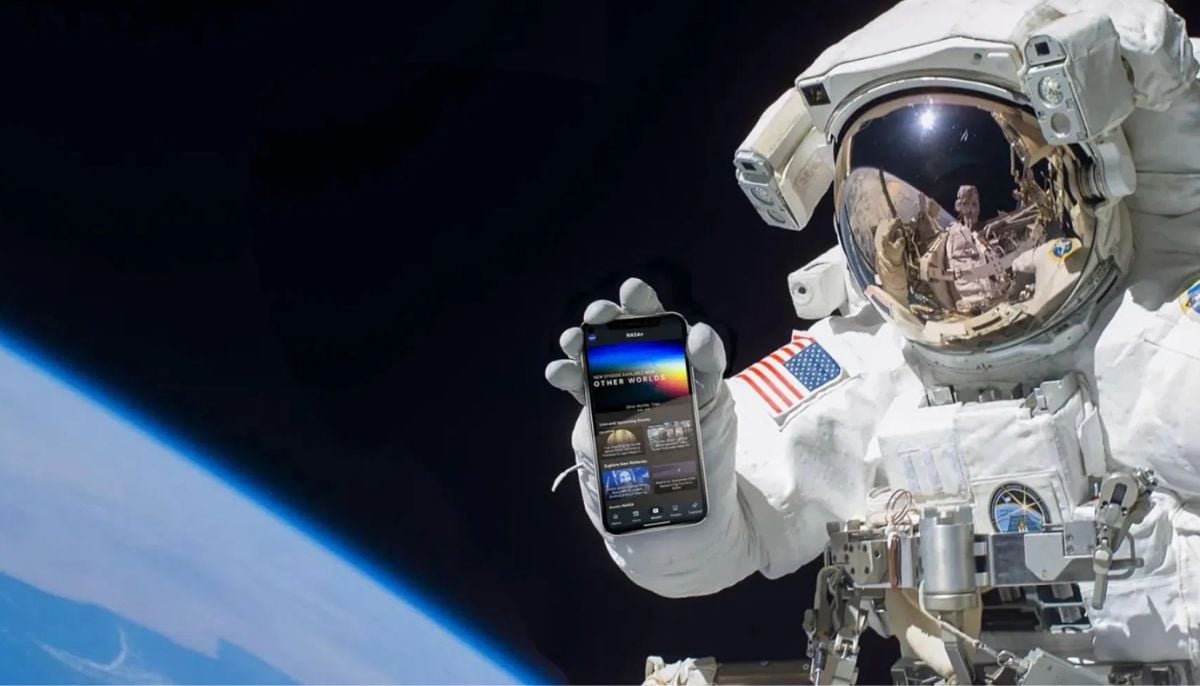
Smartphones in orbit? NASA’s Crew-12 and Artemis II missions to use latest mobile tech
-
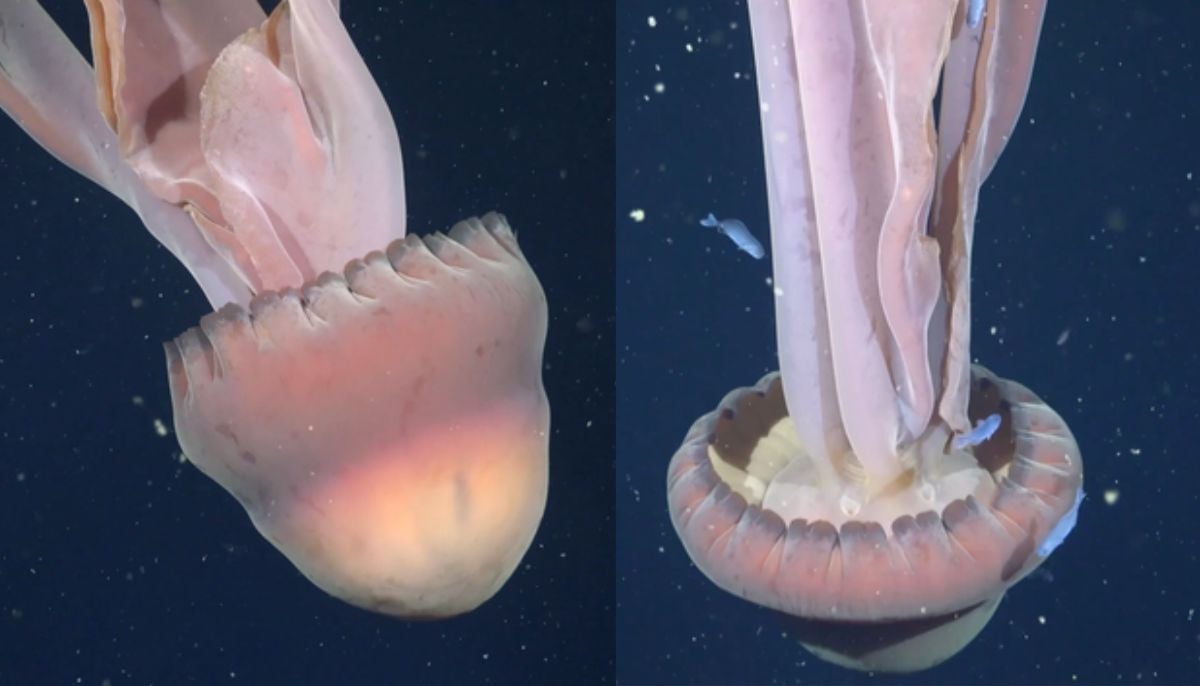
Rare deep-sea discovery: ‘School bus-size’ phantom jellyfish spotted in Argentina