W1935: Dancing lights on star-less isolated brown dwarf baffle Nasa astronomers
As per James Webb Space Telescope data, W1935 emanates infrared emissions made up of methane suggesting existence of aurora-like features
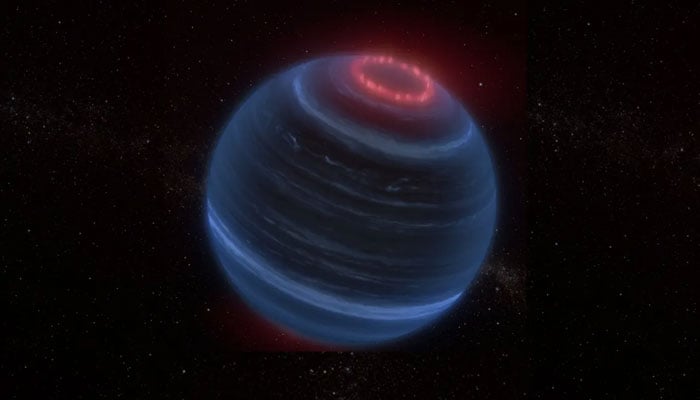
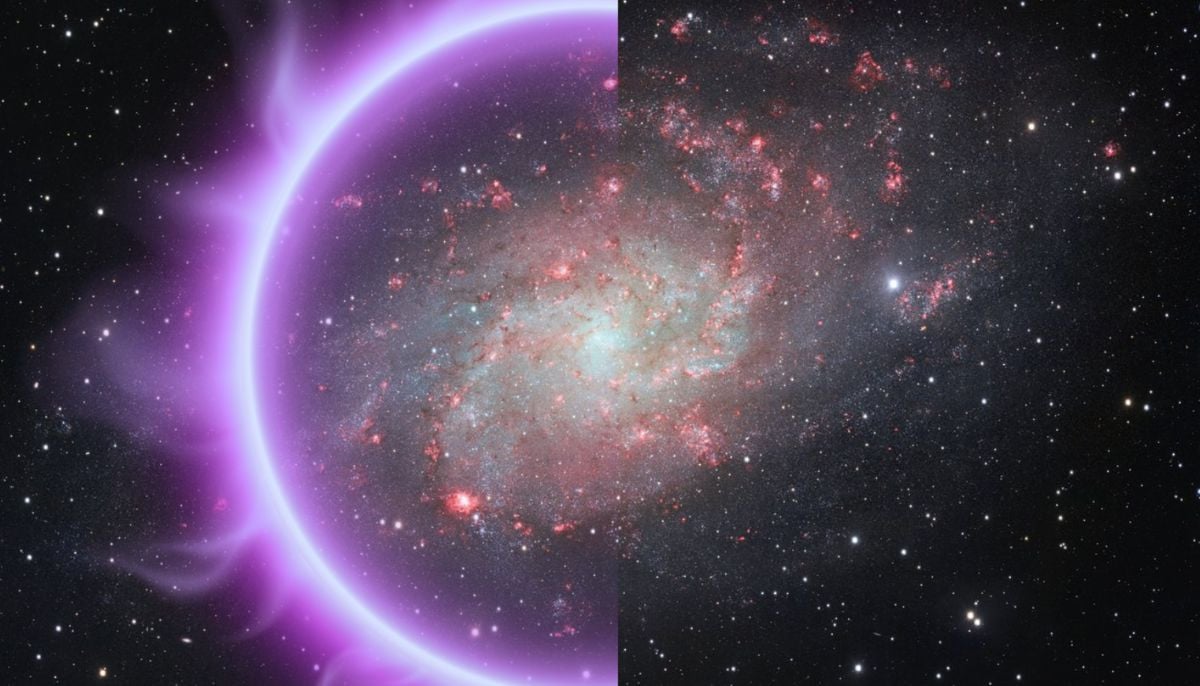
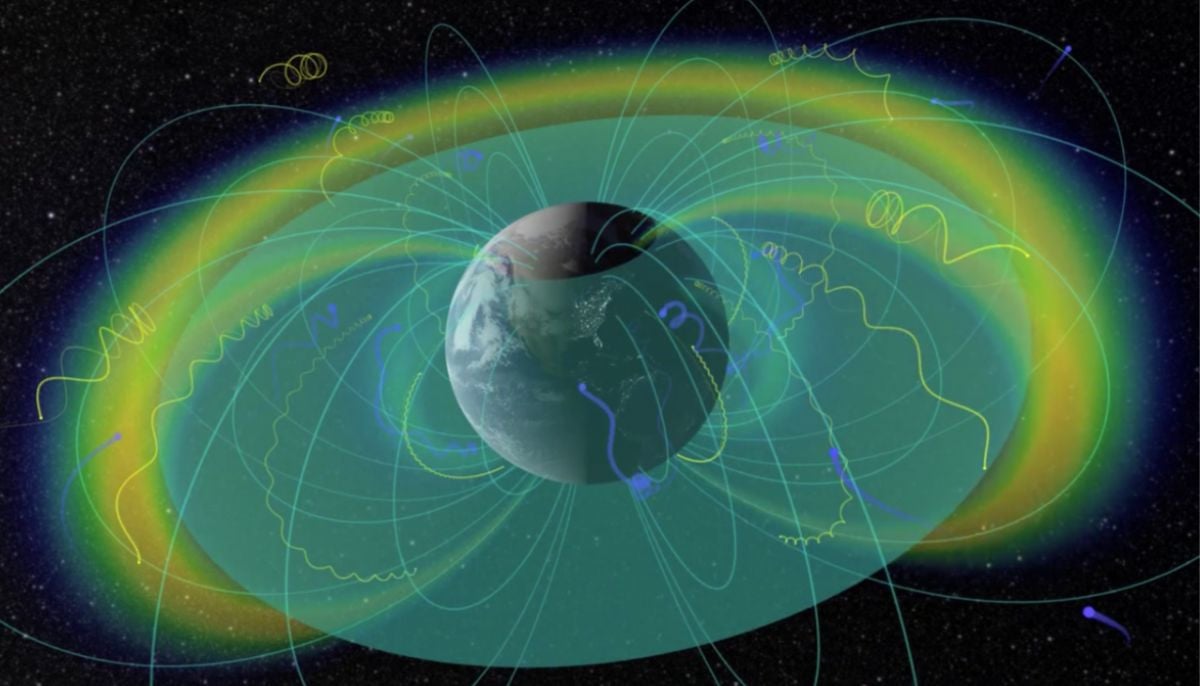
The James Webb Space Telescope has made a massive discovery, an isolated brown dwarf in space, W1935, emanating infrared emissions made up of methane suggesting a possible existence of aurora borealis-like features also known as the northern lights, reported BNN breaking.
A brown dwarf is an object bigger than the planet Jupiter but smaller than a star.
Methane emissions are a common feature in gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn. But in a brown dwarf, it is surprising, as due to our previous understanding and research, for an aurora to form it requires a host star.
As in the case of our solar system, Aurorae are formed on Earth when energetic particles from the sun interact with our planet's magnetic field, colliding with gas particles on either side of the poles creating mysterious curtains of dancing light.
Since W1935 has no star to generate a stellar wind, a team of researchers headed by Jackie Faherty has proposed that the possibility of methane around the brown dwarf could be due to interactions with either interstellar plasma or a nearby active moon.
The discovery of W1935 is significant because it raises so many questions as it the first isolated brown dwarf outside of our solar system that has auroral activity.
These findings challenge our current understanding of auroral processes and provide a new path of research into atmospheric phenomena beyond our solar system.
-
Annular solar eclipse 2026: Where and how to watch ‘ring of fire’
-
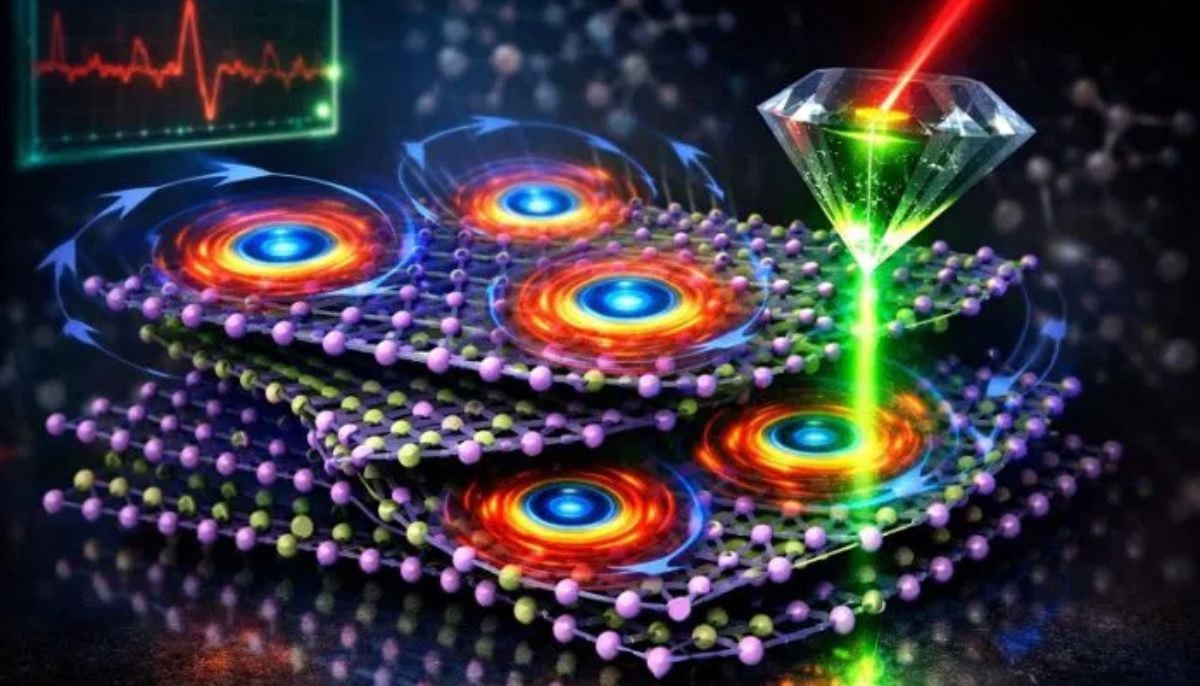
Scientists discover rare form of 'magnets' that might surprise you
-
Humans may have 33 senses, not 5: New study challenges long-held science
-
Northern Lights: Calm conditions persist amid low space weather activity
-
SpaceX pivots from Mars plans to prioritize 2027 Moon landing
-
Dutch seismologist hints at 'surprise’ quake in coming days
-
SpaceX cleared for NASA Crew-12 launch after Falcon 9 review
-
Is dark matter real? New theory proposes it could be gravity behaving strangely