Do black holes pose danger to Earth?
Scientists can't see what's inside black holes but they can observe the impact of incredible mass on its surroundings
Black holes are one of the most mysterious objects that exist in space. They are formed when a star implodes. It is also present at the centre of giant galaxies. Its gravitational pull is so powerful that any object which enters its event horizon cannot be escaped. Even light succumbs to the black hole.
The black hole contains a massive about of matter in a very small area.
The amount of mass a black hole can contain is likened to a star 10 times more massive than our sun squeezed into a sphere about as wide as New York City, said Nasa.
It also highlighted that a black hole cannot be seen directly by scientists but they can observe the impact of its incredible mass on its surroundings.
Nasa said black holes can devour stars, tearing the celestial objects apart as their powerful gravitational field pulls the stars closer.
However, scientists also underlined that that black holes can help spur the growth of new stars.
Nasa explained that if a person fell inside a black hole, the individual's perception of space and time would change. Additionally, the immense gravity of the black hole would compress you horizontally and stretch you vertically like a noodle, in a phenomenon known as "spaghettification".
How many black holes are there?
According to Nasa, in our Milky Way galaxy, there are as many as 10 million to one billion stellar black holes.
These black holes are the remnants of a massive star that collapsed and are approximately 10 to 24 times as massive as our sun.
There are other black holes that are dubbed supermassive black holes, present nearly at the centre of every giant galaxy.
According to the Space Telescope Science Institute, scientists estimate there may be about 100 billion supermassive black holes in our region of the Universe.
Sagittarius A* is present at the centre of our Milky Way galaxy. The black hole has a mass of about 4 million suns, stated Nasa.
The supermassive black hole present in our milky way is at a distance of more than 26,000 light years, or 152 quadrillion miles, away from Earth.
Nasa said: “Sagittarius A* is our closest supermassive black hole.”
In a recent discovery, astronomers had spotted the closest black hole to our planet.
National Science Foundation noted: “About 10 times more massive than the sun, the black hole is only about 1,600 light-years away. Located in the constellation Ophiuchus, the black hole is three times closer to Earth than the previous record holder.”
Scientists maintained that the nearby black hole is a dormant black hole, meaning that it is not actively feeding.
Is there any threat to Earth from any of the black holes? The answer is no because Nasa said that no black hole is close enough to be a danger to us. Additionally, the sun is not massive enough to explode to form a black hole.
-
Shanghai Fusion ‘Artificial Sun’ achieves groundbreaking results with plasma control record
-
Polar vortex ‘exceptional’ disruption: Rare shift signals extreme February winter
-
Netherlands repatriates 3500-year-old Egyptian sculpture looted during Arab Spring
-
Archaeologists recreate 3,500-year-old Egyptian perfumes for modern museums
-
Smartphones in orbit? NASA’s Crew-12 and Artemis II missions to use latest mobile tech
-
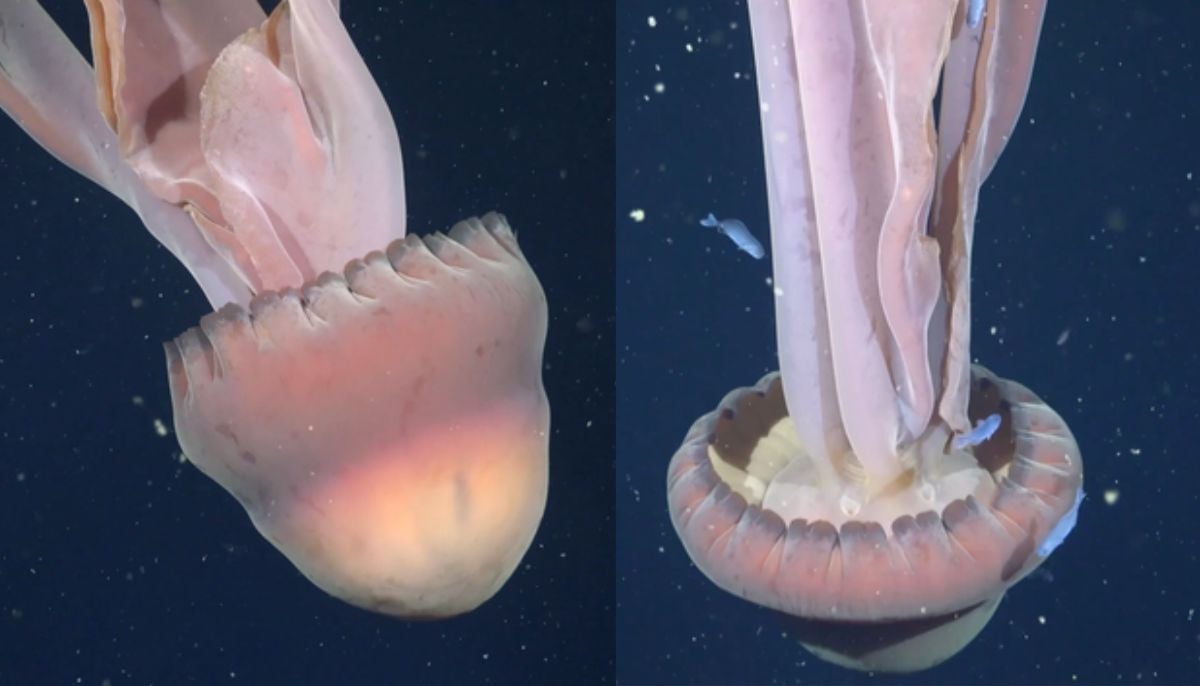
Rare deep-sea discovery: ‘School bus-size’ phantom jellyfish spotted in Argentina
-
NASA eyes March moon mission launch following test run setbacks
-
February offers 8 must-see sky events including rare eclipse and planet parade